Abstract
Background: Recent evidence supports the role of cytomegalovirus (CMV) in the development of childhood ALL. The underlying mechanism and CMV's role in the leukemic cell phenotype is unknown, but CMV typically interacts with the host immune system allowing the virus to survive in a latent state; it may be that this immune dysregulation affects the risk of ALL. This study aims to explore the association of CMV and ALL at the time of leukemia diagnosis, using AML cases as a control and further, to determine whether CMV affects certain subgroups of ALL patients such as specific ethnicities, age groups, or cytogenetic subtypes.
Methods: Pediatric diagnostic leukemia bone marrow samples obtained from the California Childhood Leukemia Study were screened for the presence of CMV DNA using a custom-designed droplet digital PCR assay. A total of 869 cases were analyzed including 125 AML cases and 744 ALL cases. Demographic and clinical features were compared between patients found to be CMV positive (cases with any detectable CMV positive droplets) and those who were CMV negative (cases with no detectable CMV positive droplets). The effect of the level of CMV viral DNA load was also assessed. For a subset of cases (n=61), Affymetrix Array gene expression data were available and differential gene expression performed to compare CMV positive cases with high viral load to CMV negative cases. Odds ratios and confidence intervals were estimated using logistic regression.
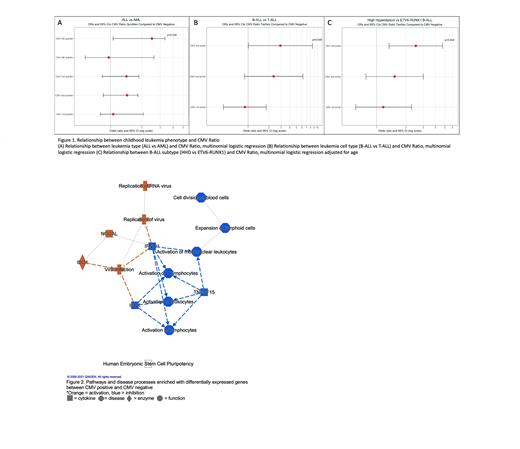
Results: ALL cases were more likely to be CMV positive compared to AML (OR: 2.50; CI 1.00, 5.47, p = 0.039 for CMV highest quintile vs. CMV negative). Within ALL cases, B-cell ALL (B-ALL) was significantly associated with CMV positivity compared to T-cell ALL (T-ALL) (OR: 2.93; CI: 1.01, 8.52, p = 0.048 for CMV highest tertile vs. CMV negative). Further subtype analysis of B-ALL cases revealed CMV positivity to be significantly associated with high hyperdiploidy, one of the most common ALL subtypes, when compared to ETV6-RUNX1 (OR: 2.52; CI:1.34, 4.73, p = 0.004 for highest CMV tertile vs. CMV negative). CMV positive B-ALL cases were also more likely to harbor deletions of EBF1, a B-cell development gene, compared to CMV negative cases (OR: 6.10; CI: 1.09, 34.06, p = 0.04 for CMV 2 nd tertile vs. CMV negative; OR: 5.54; CI: 1.13, 27.18, p = 0.03 for CMV highest tertile vs. CMV negative). Differential gene expression analysis revealed 830 genes to be significantly differentially expressed between the highest quintile of CMV positive cases and CMV negative cases, and gene ontology analysis revealed upregulation of processes involved in viral infection and replication. Specifically, cytokine signaling pathways including IL-1, IL-8, and IL-7 were upregulated in CMV positive cases while Th1 and the pathway facilitating crosstalk between dendritic cells and natural killer cells were downregulated. Interestingly, B-cell receptor signaling was also upregulated in CMV positive cases.
Conclusion: Our results support the hypothesis that CMV plays an enhanced role in leukemia development in specific subtypes of ALL, and not in AML development. The ability of CMV to interact with the host immune system, highlights immune dysregulation as a potential mechanism by which CMV contributes to risk of ALL. Gene expression analysis on a subset of cases revealed differentially expressed genes to be enriched in pathways involved in immune response, suggesting a potential role for active CMV infection in the leukemic phenotype. The patterns of up- and downregulation in these pathways were consistent with the host response to CMV. Additionally, acute CMV infection has been shown to promote B-cell activation and proliferation. Further, CMV seropositive individuals have been reported to have altered immune responses even with the virus in a latent state highlighting the virus's effect on B-cells. In our study we also found B-cell receptor signaling to be upregulated in CMV positive cases. This is consistent with the known effects of CMV in a typical host, but in patients with leukemia it provides an interesting potential link between CMV infection and development of pediatric ALL. These intriguing results require validation and warrant continued investigation of the role of CMV in pediatric leukemia development.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal